Development and Tech Transfer of Multi-agent Virtual Simulation Testbed Ecosystem
As cities grow and new transportation alternatives and technologies emerge, the complexity of managing urban transportation systems increases as well. Transportation policymakers and agency leaders need models that can support time-sensitive planning, operation control and policy implementation. C2SMART is working to fill this need through the development of an open-source, large-scale microscopic transportation model that covers the entire New York City area and integrates data and modeling capabilities for new technologies such as connected and autonomous vehicles, electric vehicles, dockless bikes, and ridesharing systems.
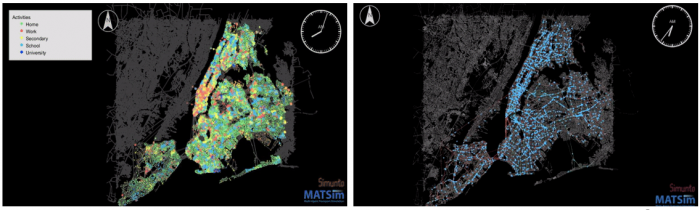
In previous years, the research team has developed and calibrated a base model implemented in MATSim and SUMO. This virtual testbed simulates an 8-million-person population and includes cars, trains, bus, bikeshare, taxi, and other for-hire vehicles calibrated to the year 2016. The team is building the architecture to host this virtual test bed and developing system design and user guide documentation. In addition, the models are being applied to evaluate specific projects like the effects of connected vehicles on safety along a key corridor in downtown Brooklyn or to evaluate the effects of the planned congestion pricing policy and the use of carsharing fleets. In this phase of the project, the virtual testbed will be enhanced to incorporate more applications for emerging mobility services and the team will develop a web-based interface for the ecosystem. The research team will also seek to connect with and train potential users, such as policymakers and other researchers, to encourage adoption of the virtual testbed for real-world use and new research applications.
MATSim in Action
COVID-19 Recovery and Congestion Pricing
The open-source, modular nature of the Multi-Agent Transport Simulation (MATSim) Virtual Testbed has allowed a team of researchers led by Dr. Joseph Chow and Yueshuai Brian He to add timely new simulation extensions: the impact of congestion pricing on transit behavior and MTA revenues, and the effects of the pandemic and an ensuing recovery on transit use.
A Pandemic Recovery Plan
How will transit patterns change as New York City begins to reopen in stages? Researchers recalibrated the simulation testbed to evaluate the impact of COVID-19 on mass transit ridership, demonstrating how MATSIM might be used to help policy-makers plan for reopening.
Using Apple Mobility Trends Reports, MTA Transit Data and NAICS industry codes, the research team recalibrated mode choice to fit updated ridership data and account for the shift to cars during the COVID-19 pandemic. The team will simulate a multi-stage recovery on the synthetic population by “reopening” manufacturing/construction industries while keeping schools and nonessential businesses close, mirroring governor Andrew Cuomo’s stated plan for reopening New York City.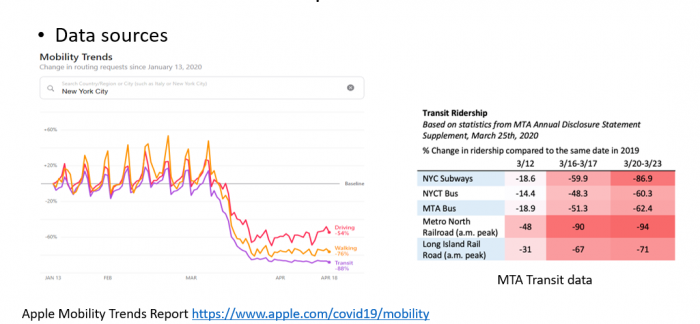
Congestion Pricing
How will NYC’s plan to charge congestion pricing south of 60th Street relieve congestion in Manhattan and raise public transit funds? How much should drivers be charged? Researchers used MATSIM to evaluate two price schemes to see how each would affect traffic and mode-shift from between transportation forms, along with impacts on consumer surplus and MTA revenue.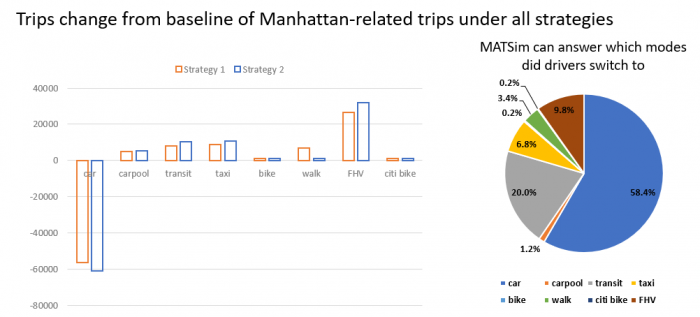
Other Applications
MATSim Applications for Policy-Makers
Click to watch Joseph Chow and Yuehuai Brian He discuss their project’s applications for policy-makers. Webinar delivered on 4/29/2020
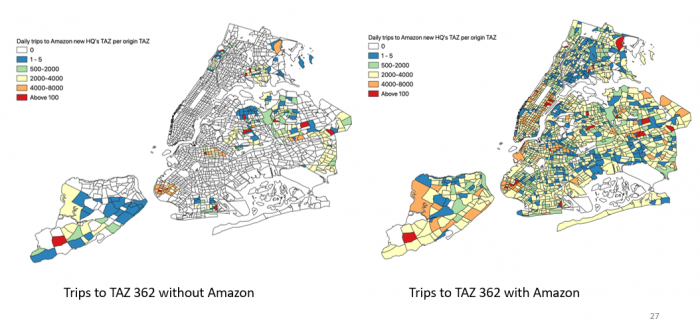
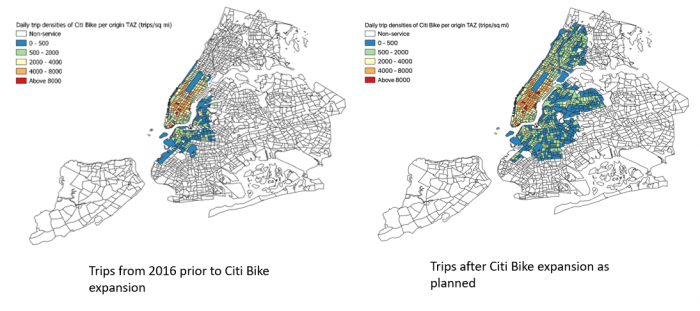
Simulation of the impact of an Amazon HQ in New York on modal trips
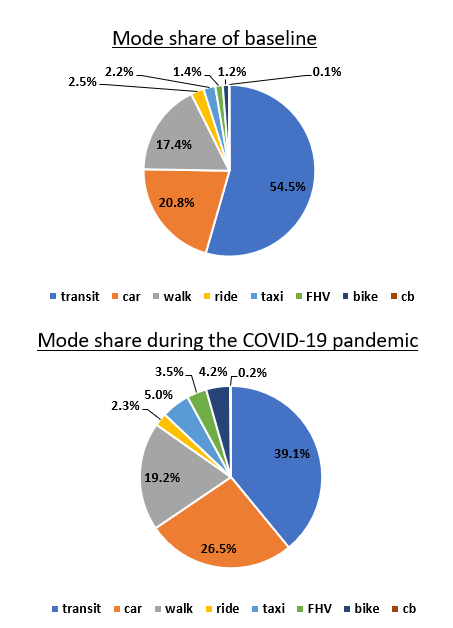
Recalibrated mode-shift due to COVID-19 Pandemic
Background
Building on the development of the testbed in previous years, this project will further enhance its applicability and aim to transfer knowledge for using the testbed to local agencies and other members of the C2SMART consortium. The objectives for this phase include:
Application Enhancements
- Use of direct extensions using the base model, such as automated and connected taxis and dockless bikeshare. Different deployment scenarios will be evaluated to provide decision support capabilities to transportation agencies
- Develop a new integrated web-based data analytics toolbox to allow researchers to analyze extensive output of MATSim
- Modification of traffic flow model in MATSim to improve consistency with SUMO and connected vehicle technology in a new model instance
- Test and implement multimodal travel capability using the R5 routing engine adopted by BEAM for a new model instance
Technology Transfer
- Publish a web interface for the virtual testbed
- Open a beta testing period and invite participants from local agencies to evaluate and provide feedback
- Host webinars to share lessons learned in procedures for developing MATSim models and integrating with SUMO with students and PIs at consortium member universities, which will support the expansion of the testbed to other cities
Deliverables
- Simulated scenarios of automated and connected taxi and dockless bikeshare using base model
- Alternative base model with updated traffic flow model with connected vehicle penetration rate
- Alternative base model with multimodal routing
- Ecosystem web interface
- Lesson plans for NYC DOT staff
Final Report
| Principal Investigator | Joseph Chow, NYU |
| Funding Source | C2SMART Center: $81,999 NYU (cost-share): $47,198 |
| Total Project Cost | $135,799 |
| USDOT Award # | 69A3551747124 |
| Start and End Dates | 03/01/2019-05/31/2020 |
| Implementation of Research Outcomes | The research will produce simulation outcomes for several scenarios of interest to DOT and include activities that make the test bed accessible to policymakers and consortium partners. |
| Impacts/Benefits of Implementation | The research will provide resources and a virtual framework for supporting and helping public sector’s decision making to fill in the gap between basic research and field deployment. Subsequent implementations of the test bed in other cities will form the basis for a “Network of Living Labs” that NYC DOT and other local agencies can benefit from shared knowledge transfer. |